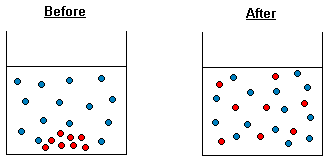
Diffusion is the seemingly random movement of a substance from where these particles are in high concentration to where there are fewer. The diffusion stops where there is no concentration gradient existing.
This means that the concentration is the same everywhere in the solution as shown in the second beaker in the diagram below, after diffusion has occurred.
Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water. A semi-permeable membrane is a membrane that has pores (small holes) in it to allow certain sized molecules through.
Osmosis has a large role to play in the lives of both plants and mammals. Red blood cells have no rigid cell wall, therefore if they are put into a very dilute solution (lots of water – low concentration) they will fill up with water and eventually burst.
This could obviously be fatal if allowed to carry on in the body.
This does not happen though because the blood water levels are kept constant by the process of homeostasis. The kidneys are the main regulator of the amount of water in the blood as well as other substances.
Diffusion of water as a gas also takes place in plants in their leaves. This is part of the transpiration stream where water is taken up through the roots of the plant and eventually released into the atmosphere.
