The general formula for alkanes is as follows:
- CnH2n+2 (where “n” is a constant)
The first ten members of the homologous series of the alkanes are:
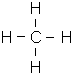
- CH4 (Methane)
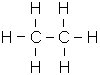
- C2H6 (Ethane)
- C3H8 (Propane)
- C4H10 (Butane)
- C5H12 (Pentane)
- C6H14 (Hexane)
- C7H16 (Heptane)
- C8H18 (Octane)
- C9H20 (Nonane)
- C10H22 (Decane)
Alkanes consist of strong covalent bonds therefore they are, on the whole, quite un-reactive. They do not react with acids, alkalis, and oxidising agents. Their most important reaction is that of combustion.
The main chemical reactions that alkanes undergo are:
- Combustion
- Substitution with halogens
- Catalytic Cracking