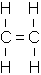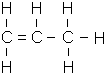The general formula for alkenes is as follows:
- CnH2n (where “n” is a constant)
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons because they contain a double bond between two of their carbon atoms. The simplest alkene is ethene (C2H4) because “methene” (CH2) cannot exist.
The first four members of the homologous series of the alkenes are:
- C2H4 (Ethene – Gas at room temperature/pressure)
- C3H6 (Propene – Gas at room temperature/pressure)
- C4H8 (Butene – Gas at room temperature/pressure)
- C5H10 (Pentene – Liquid at room temperature/pressure)